reshape2 is an
R package written by Hadley Wickham that makes it easy
to transform data between wide and long formats.
What makes data wide or long?
Wide data has a column for each variable. For example, this is wide-format data:
## ozone wind temp
## 1 23.61538 11.622581 65.54839
## 2 29.44444 10.266667 79.10000
## 3 59.11538 8.941935 83.90323
## 4 59.96154 8.793548 83.96774And this is long-format data:
## No id variables; using all as measure variables## variable value
## 1 ozone 23.615385
## 2 ozone 29.444444
## 3 ozone 59.115385
## 4 ozone 59.961538
## 5 wind 11.622581
## 6 wind 10.266667
## 7 wind 8.941935
## 8 wind 8.793548
## 9 temp 65.548387
## 10 temp 79.100000
## 11 temp 83.903226
## 12 temp 83.967742Long-format data has a column for possible variable types and a column for the values of those variables. Long-format data isn’t necessarily only two columns. For example, we might have ozone measurements for each day of the year. In that case, we could have another column for day. In other words, there are different levels of “longness”. The ultimate shape you want to get your data into will depend on what you are doing with it.
It turns out that you need wide-format data for some types of data analysis
and long-format data for others. In reality, you need long-format data much
more commonly than wide-format data. For example, ggplot2 requires
long-format data
(technically tidy data),
plyr requires long-format data, and most modelling functions (such as
lm(), glm(), and gam()) require long-format data. But people often find
it easier to record their data in wide format.
The reshape2 package
reshape2 is based around two key functions: melt and cast:
melt takes wide-format data and melts it into long-format data.
cast takes long-format data and casts it into wide-format data.
Think of working with metal: if you melt metal, it drips and becomes long. If you cast it into a mould, it becomes wide.
Wide- to long-format data: the melt function
For this example we’ll work with the airquality dataset that is built
into R. First we’ll change the column names to lower case to make them
easier to work with. Then we’ll look at the data:
names(airquality) <- tolower(names(airquality))
head(airquality)## ozone solar.r wind temp month day
## 1 41 190 7.4 67 5 1
## 2 36 118 8.0 72 5 2
## 3 12 149 12.6 74 5 3
## 4 18 313 11.5 62 5 4
## 5 NA NA 14.3 56 5 5
## 6 28 NA 14.9 66 5 6What happens if we run the function melt with all the default argument
values?
aql <- melt(airquality) # [a]ir [q]uality [l]ong format## No id variables; using all as measure variableshead(aql)## variable value
## 1 ozone 41
## 2 ozone 36
## 3 ozone 12
## 4 ozone 18
## 5 ozone NA
## 6 ozone 28tail(aql)## variable value
## 913 day 25
## 914 day 26
## 915 day 27
## 916 day 28
## 917 day 29
## 918 day 30By default, melt has assumed that all columns with numeric values are
variables with values. Often this is what you want. Maybe here we want
to know the values of ozone, solar.r, wind, and temp for each
month and day. We can do that with melt by telling it that we want
month and day to be “ID variables”. ID variables are the variables
that identify individual rows of data.
aql <- melt(airquality, id.vars = c("month", "day"))
head(aql)## month day variable value
## 1 5 1 ozone 41
## 2 5 2 ozone 36
## 3 5 3 ozone 12
## 4 5 4 ozone 18
## 5 5 5 ozone NA
## 6 5 6 ozone 28What if we wanted to control the column names in our long-format data?
melt lets us set those too all in one step:
aql <- melt(airquality, id.vars = c("month", "day"),
variable.name = "climate_variable",
value.name = "climate_value")
head(aql)## month day climate_variable climate_value
## 1 5 1 ozone 41
## 2 5 2 ozone 36
## 3 5 3 ozone 12
## 4 5 4 ozone 18
## 5 5 5 ozone NA
## 6 5 6 ozone 28Long- to wide-format data: the cast functions
Whereas going from wide- to long-format data is pretty straightforward, going from long- to wide-format data can take a bit more thought. It usually involves some head scratching and some trial and error for all but the simplest cases. Let’s go through some examples.
In reshape2 there are multiple cast functions. Since you will most
commonly work with data.frame objects, we’ll explore the
dcast function. (There is also acast to return a vector, matrix, or
array.)
Let’s take the long-format airquality data and cast it into some
different wide formats. To start with, we’ll recover the same format we
started with and compare the two.
dcast uses a formula to describe the shape of the data. The arguments
on the left refer to the ID variables and the arguments on the right
refer to the measured variables. Coming up with the right formula can
take some trial and error at first. So, if you’re stuck don’t feel bad
about just experimenting with formulas. There are usually only so many
ways you can write the formula.
Here, we need to tell dcast that month and day are the ID
variables (we want a column for each) and that variable describes the
measured variables. Since there is only one remaining column,
dcast will figure out that it contains the values themselves. We could
explicitly declare this with value.var. (And in some cases it will be
necessary to do so.)
aql <- melt(airquality, id.vars = c("month", "day"))
aqw <- dcast(aql, month + day ~ variable)
head(aqw)## month day ozone solar.r wind temp
## 1 5 1 41 190 7.4 67
## 2 5 2 36 118 8.0 72
## 3 5 3 12 149 12.6 74
## 4 5 4 18 313 11.5 62
## 5 5 5 NA NA 14.3 56
## 6 5 6 28 NA 14.9 66head(airquality) # original data## ozone solar.r wind temp month day
## 1 41 190 7.4 67 5 1
## 2 36 118 8.0 72 5 2
## 3 12 149 12.6 74 5 3
## 4 18 313 11.5 62 5 4
## 5 NA NA 14.3 56 5 5
## 6 28 NA 14.9 66 5 6So, besides re-arranging the columns, we’ve recovered our original data.
If it isn’t clear to you what just happened there, then have a look at this illustration:
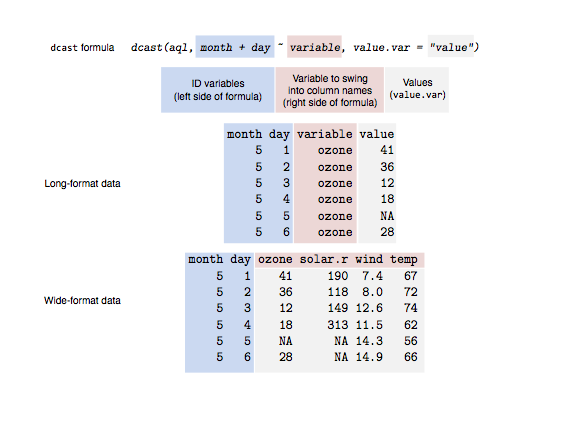
Figure 1: An illustration of the dcast function. The blue shading indicates
ID variables that we want to represent individual rows. The red shading
represents variable names that we want to swing into column names. The grey
shading represents the data values that we want to fill in the cells with.
One confusing “mistake” you might make is casting a dataset in which
there is more than one value per data cell. For example, this time we
won’t include day as an ID variable:
dcast(aql, month ~ variable)## Aggregation function missing: defaulting to length## month ozone solar.r wind temp
## 1 5 31 31 31 31
## 2 6 30 30 30 30
## 3 7 31 31 31 31
## 4 8 31 31 31 31
## 5 9 30 30 30 30When you run this in R, you’ll notice the warning message:
# Aggregation function missing: defaulting to lengthAnd if you look at the output, the cells are filled with the number of
data rows for each month-climate combination. The numbers we’re seeing
are the number of days recorded in each month. When you cast your data
and there are multiple values per cell, you also need to tell
dcast how to aggregate the data. For example, maybe you want to take
the mean, or the median, or the sum. Let’s try the last example,
but this time we’ll take the mean of the climate values. We’ll also pass
the option na.rm = TRUE through the ... argument to remove NA
values. (The ... let’s you pass on additional arguments to your
fun.aggregate function, here mean.)
dcast(aql, month ~ variable, fun.aggregate = mean,
na.rm = TRUE)## month ozone solar.r wind temp
## 1 5 23.61538 181.2963 11.622581 65.54839
## 2 6 29.44444 190.1667 10.266667 79.10000
## 3 7 59.11538 216.4839 8.941935 83.90323
## 4 8 59.96154 171.8571 8.793548 83.96774
## 5 9 31.44828 167.4333 10.180000 76.90000Unlike melt, there are some other fancy things you can do with
dcast that I’m not covering here. It’s worth reading the help file
?dcast. For example, you can compute summaries for rows and columns,
subset the columns, and fill in missing cells in one call to dcast.
Additional help
Read the package help:
help(package = "reshape2")
See the reshape2 website:
http://had.co.nz/reshape/
And read the paper on reshape:
Wickham, H. (2007). Reshaping data with the reshape package.
21(12):1–20.
http://www.jstatsoft.org/v21/i12
(But note that the paper is written for the reshape package not the
reshape2 package.)